Future Metals
Niobium
Niobium plays a significant role in enhancing the properties of materials used in a wide range of industries. Its applications in steel production, superalloys, and superconducting technologies underline its importance in the modern economy.
Niobium plays a significant role in enhancing the properties of materials used in a wide range of industries. Its applications in steel production, superalloys, and superconducting technologies underline its importance in the modern economy. With the demand for high-performance and sustainable materials on the rise, the niobium market is poised for continued growth, making it a key component of future technological advancements.
One of the most critical uses of niobium is in the steel industry as a micro-alloying element. Even small amounts of niobium added to steel significantly enhance its strength and resistance to wear and corrosion, making it essential in many industries, particularly the defence, automotive and aerospace industries. In these sectors, the need for high-strength, lightweight materials is paramount to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Niobium is key to the production of superalloys which can withstand extreme temperatures and stresses, making them ideal for use in jet engines, gas turbines, and space exploration. Additionally, niobium's superconducting properties are exploited in the manufacturing of superconducting magnets, which are critical in medical imaging technologies such as MRI machines, as well as in scientific research facilities.
The Niobium Market
The niobium market is relatively small but highly concentrated, with Brazil being the largest producer, accounting for over 90% of global production1. The leading mining companies in Brazil, such as CBMM (Companhia Brasileira de Metalurgia e Mineração), dominate the market, ensuring a steady supply of this crucial element. Canada and Australia also have significant niobium reserves and production capabilities, contributing to the global supply.
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Demand for niobium has been steadily increasing due to its growing use in various high-performance applications. The steel industry's shift towards high-strength, low-alloy (HSLA) steels, which require niobium, has been a significant driver of this demand. Additionally, advancements in technology and the push for more efficient and sustainable materials in the automotive and aerospace industries have further boosted niobium's importance.
Niobium is a strategically important material and nations are actively attempting to diversify supply chains and develop new mining projects to ensure market stability. Moreover, as industries continue to seek materials that offer superior performance and sustainability, the importance of niobium is likely to grow, further influencing its market dynamics and prices.
US Geological Survey https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2022/mcs2022-niobium.pdf
Tantalum
Tantalum is highly resistant to corrosion and has excellent conductive properties, making it indispensable in various high-tech and industrial applications. Tantalum is relatively rare in the Earth's crust, with an average concentration of about 2 parts per million.
Tantalum is highly resistant to corrosion and has excellent conductive properties, making it indispensable in various high-tech and industrial applications. Tantalum is relatively rare in the Earth's crust, with an average concentration of about 2 parts per million1. It always occurs in nature with Niobium2 and is mainly sourced from the mineral columbite-tantalite (coltan), which is found in Australia, Brazil, Canada, and parts of Africa. Despite its scarcity, the high demand for tantalum in the electronics industry drives extensive mining and recycling efforts to secure adequate supply.
In the aerospace and defense industries, tantalum is used in the production of superalloys, which are employed in jet engines, missile components, and other high-stress applications. Its high melting point and strength at elevated temperatures enhance the performance and durability of these critical components.
Tantalum's primary use is in the electronics industry. Its ability to form an extremely thin oxide coating which provides a protection layer makes tantalum the material of choice in the production of small, high-quality capacitors3. Tantalum capacitors are preferred in applications that require high reliability and performance, such as in smartphones, laptops, and automotive electronics. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for use in medical implants, such as surgical instruments, prosthetic devices, and dental equipment. Tantalum's biocompatibility ensures it does not react adversely with body tissues, making it a preferred material in the medical field.
Tantalum Market
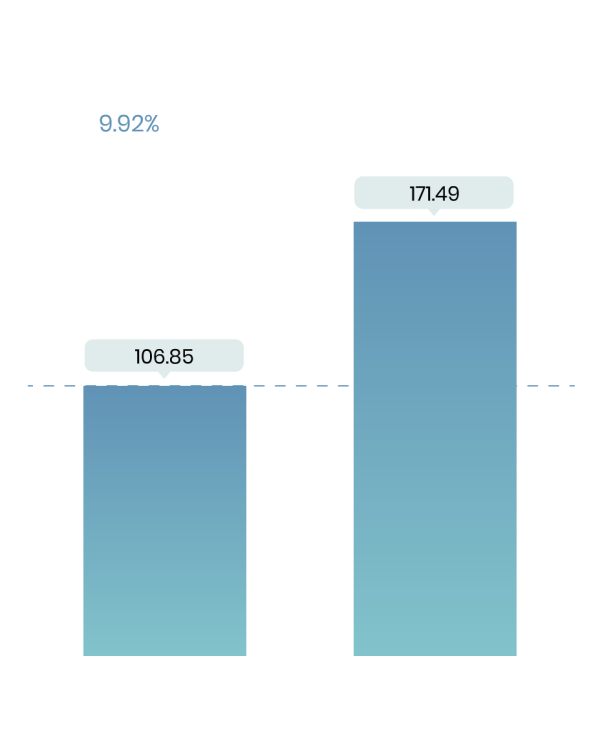
The global tantalum market size was worth around USD 521.47 million in 2022 and is predicted to grow to around USD 798.65 million by 2030 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 5.88% between 2023 and 20304. The global market is driven by its extensive use in the electronics and aerospace industries. As of recent years, the market has been characterized by fluctuations in supply due to geopolitical factors and varying production levels. The Democratic Republic of the Congo, a major producer, has faced challenges related to mining practices and regulatory changes, impacting global supply chains.
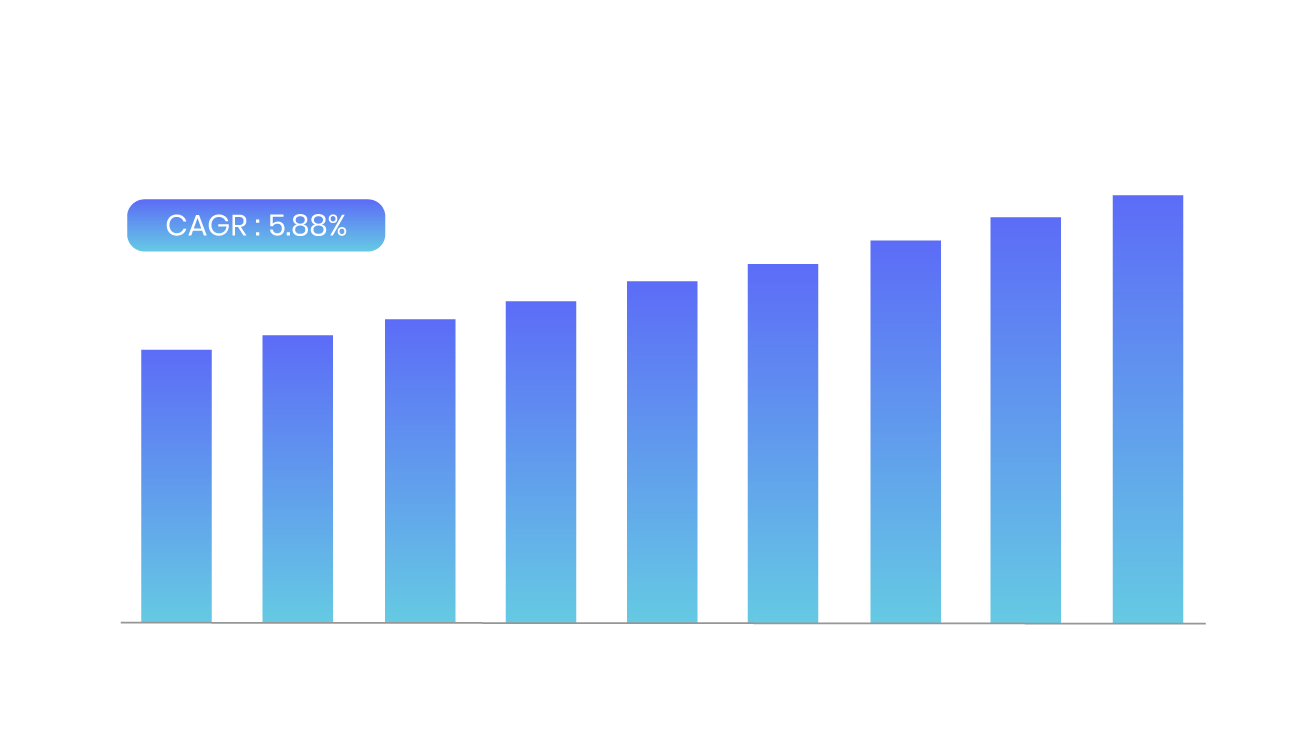
Source: Zion Market research
Prices for tantalum have experienced volatility, reflecting the balance between demand from high-tech industries and supply constraints. Efforts to recycle tantalum from electronic waste have increased, contributing to the supply but not fully offsetting the demand from new sources.
Overall, the tantalum market is expected to grow as the demand for electronic devices, medical implants, and aerospace components continues to rise, driving further exploration and development of new tantalum resources globally.
1. What are the uses of Tantalum 2. Stanford Advanced Materials: Where is Tantalum Mined 3. Tantalum: Mineral Resource spotlight 4. Tantalum Market Size, Share, Growth, Forecast 2030
Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 metallic elements, including scandium, yttrium, and the 15 lanthanides. These elements are critical to a wide range of high-tech applications and industries due to their unique chemical and physical properties.
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 metallic elements, including scandium, yttrium, and the 15 lanthanides. These elements are critical to a wide range of high-tech applications and industries due to their unique chemical and physical properties. One key metric used to evaluate the content of rare earth elements is Total Rare Earth Oxides (TREO), which measures the concentration of rare earth oxides in a given material. TREO is essential for determining the economic viability of rare earth deposits and for assessing their potential uses in various applications.
REE Applications
Rare earth elements play a pivotal role in modern technology and industry. The measurement of TREO (total rare earth oxides) is essential for evaluating the potential of rare earth deposits and their applications. With the growing demand for REEs driven by advancements in technology and the global push for sustainable energy, addressing supply issues and stabilizing the market are crucial. As new players like Brazil enter the market, there is hope for a more diversified and resilient supply chain, ensuring the continued availability of these critical elements for future technological advancements.
REEs are indispensable in the production of high-performance permanent magnets, which are crucial for electrification technologies such as electric vehicle (EV) motors and wind turbine generators. They are also vital in various defense applications, including guidance systems, lasers, and communication devices. In addition to these uses, rare earth elements are critical components in the manufacturing of smartphones, LED displays, and numerous other electronic devices.
Global Supply
China accounts for around 60% of global rare earth mined production, 85% of processing capacity, and manufactures over 90% of high-strength rare earth permanent magnets1. This concentration poses significant supply risks for other countries and industries that depend on these critical materials.
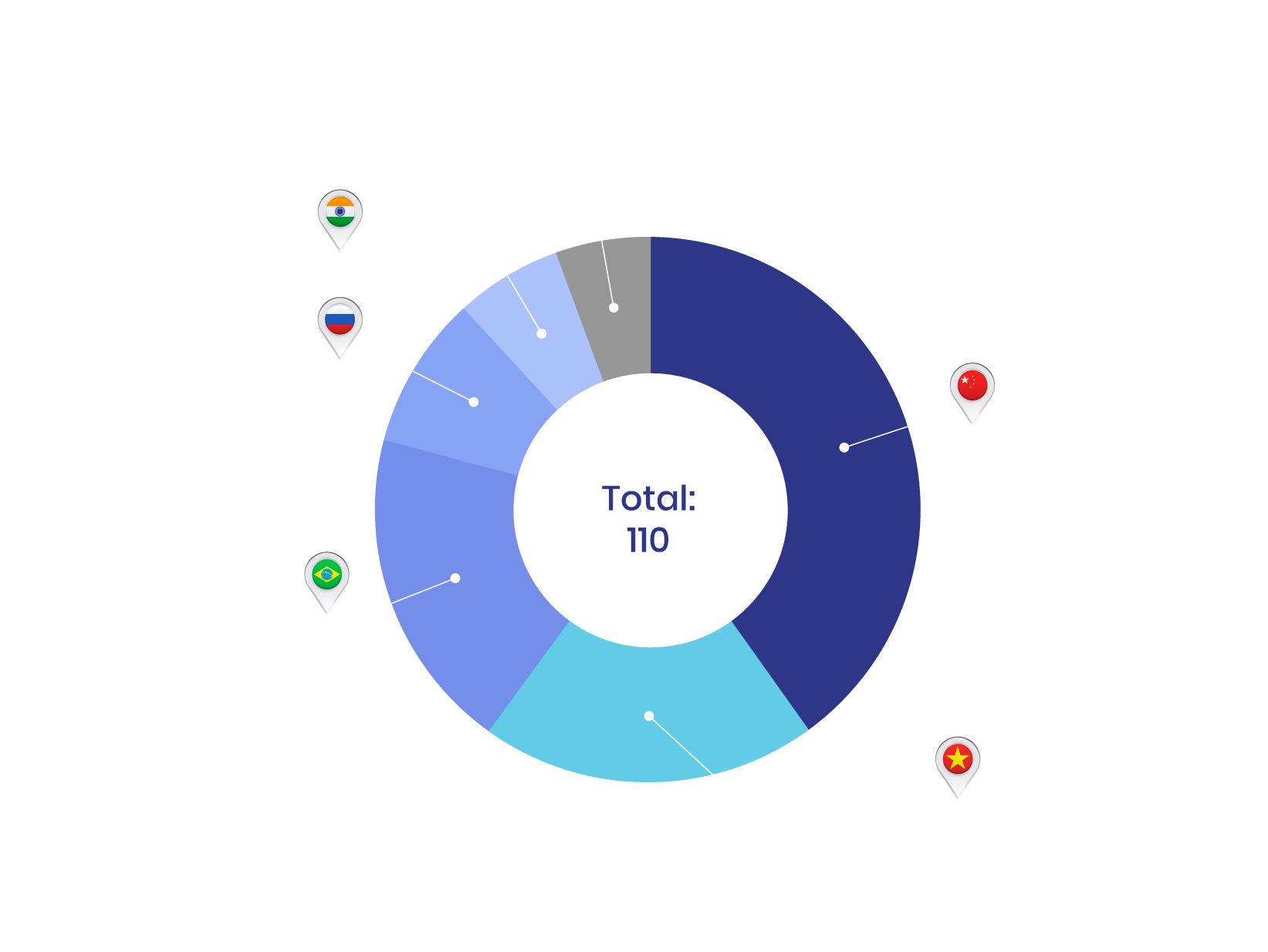
Source: US Geological Survey via Reuters
Brazil is emerging as a significant player in the rare earth market, with substantial reserves and increasing production capabilities. It is estimated that Brazil holds the world's third-largest rare earth reserve2. Diversification of the REE market is crucial for reducing the global reliance on Chinese supplies, stabilizing the market, and providing nations with domestic energy security.
REE Market Forecasts
From 2022 through 2035, it is anticipated that the value of rare earth oxides consumed by energy-transition-related applications will rise at a CAGR of 19.1%, from $3.8 billion in 2022 to $36.2 billion in 20353.
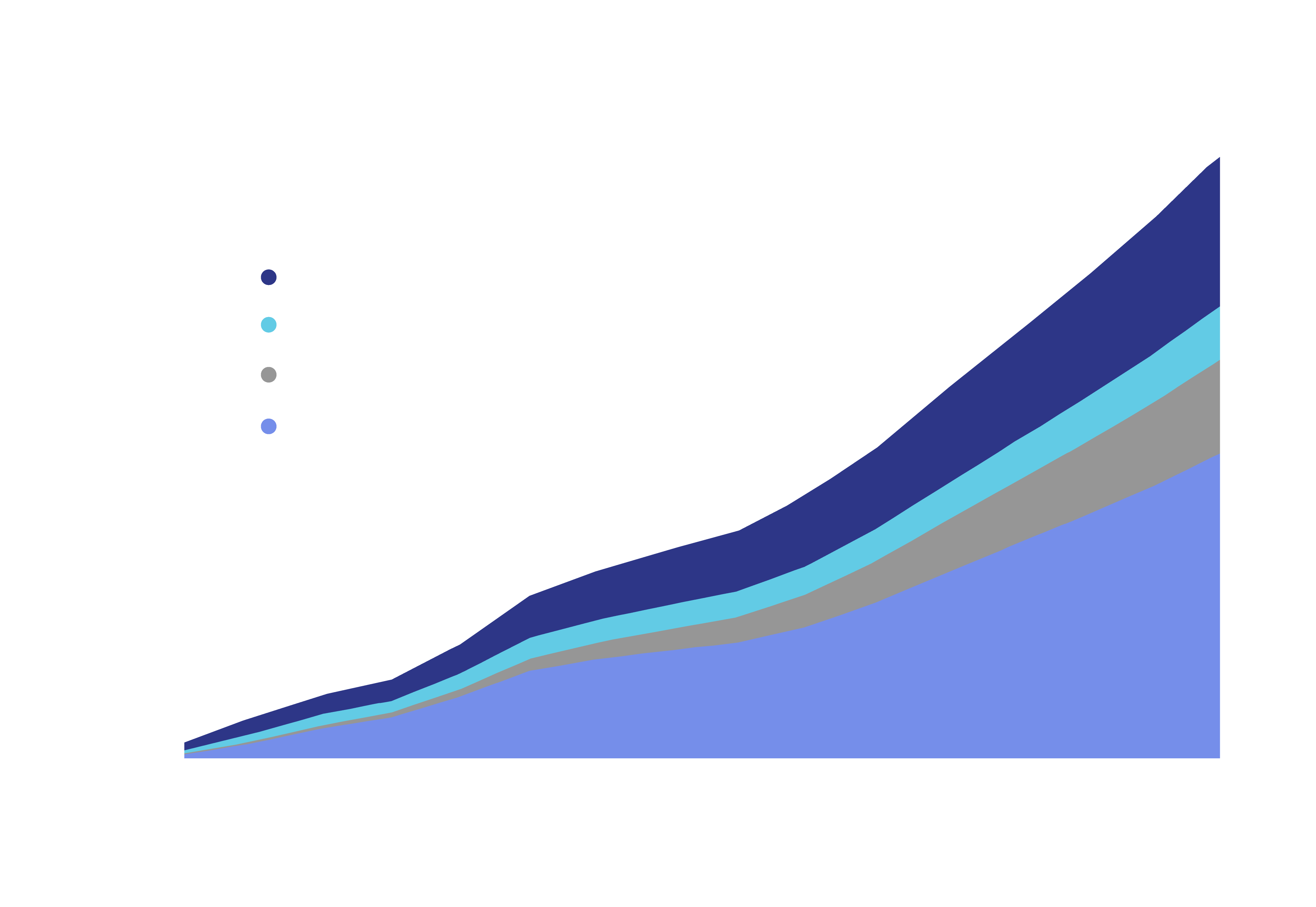
Source: Adamas Intelligence
Given that orders from automotive and wind energy companies are accelerating, the global demand for magnet rare earths is expected to reach 466 kilotons by 2035, up from 170 kilotons in 2022, a threefold increase that amounts to an 8% compound annual growth rate4. This anticipated shortfall underscores the urgency of developing new sources and improving the efficiency of existing supply chains to support the growing demand. It is estimated that more than 20 new rare-earth projects need to be launched between now and 2030, with an additional 10 projects needed by 20354.
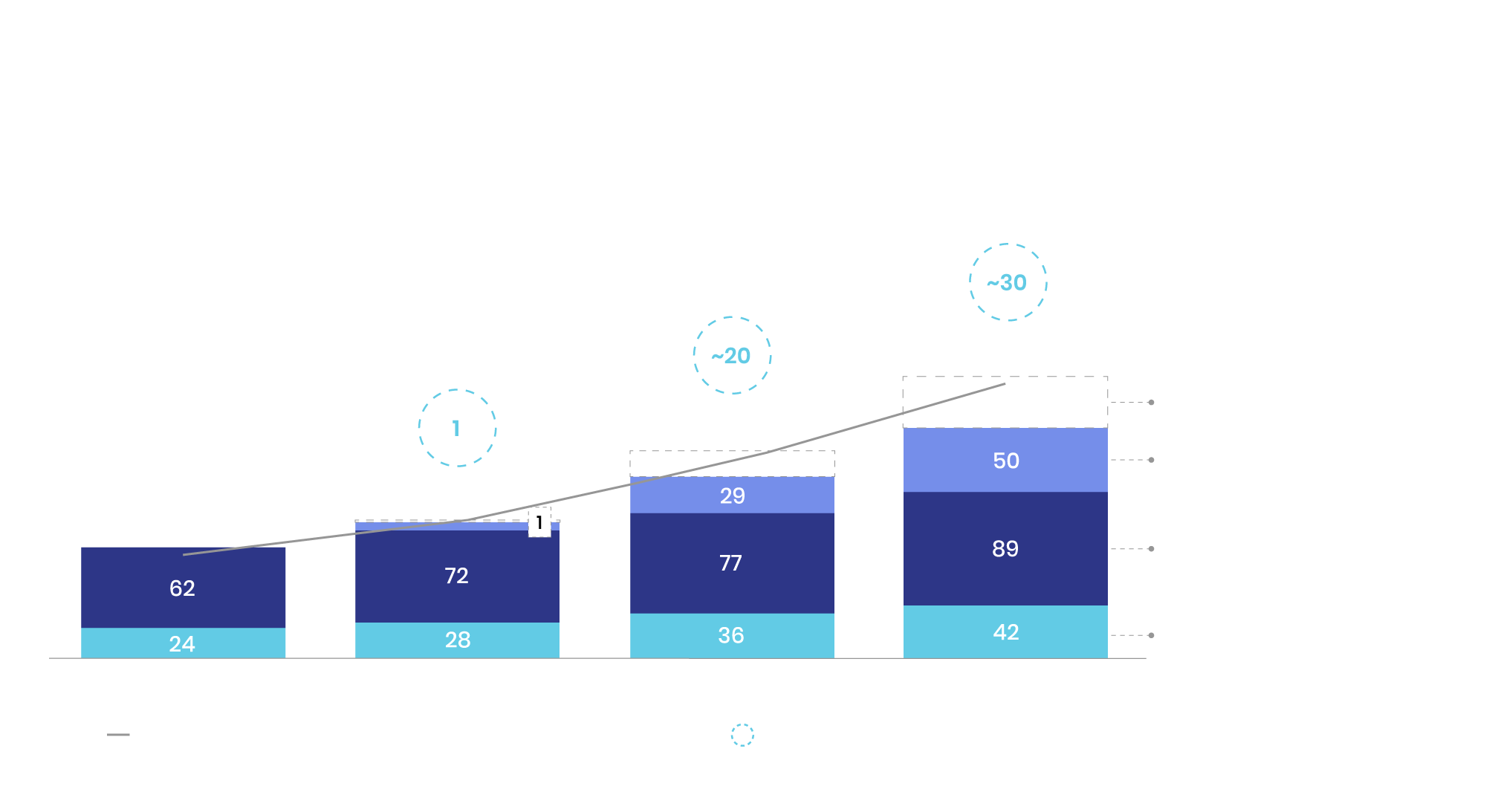
Source: Boston Consulting Group
1. Politico: China Dominates the Rare Earths Market 2. Brazil joins race to loosen China's grip on rare earths industry 3. The Skyrocketing Value of Rare Earths Powering the Energy Transition 4.Five Steps for Solving the Rare-Earth Metals Shortage
Lithium
Lithium is in high demand as we transition to a battery-powered future, yet it's a finite resource. From 2017 to 2022, the energy sector's demand was a key driver behind a threefold increase in overall demand for lithium, a 70% rise in cobalt demand, and a 40% increase in nickel demand.
Lithium is in high demand as we transition to a battery-powered future, yet it's a finite resource.
From 2017 to 2022, the energy sector's demand was a key driver behind a threefold increase in overall demand for lithium, a 70% rise in cobalt demand, and a 40% increase in nickel demand. In 2022, clean energy applications accounted for 56% of total lithium demand1.
Lithium is predominately mined in Latin America and Australia, with China dominating processing. Production of lithium chemicals and products spans countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, making the supply chain global. The U.S., Australia and allied Western nations depend on factors beyond their control for the supply of processed lithium, like global prices, foreign mining and geopolitical factors.
While global lithium reserves theoretically meet rising demand, challenges exist. Few companies can produce high-quality lithium products, and expansion projects may not meet demand swiftly. Moreover, developing lithium mines takes time, with an average of 16.5 years for those starting between 2010 and 2019, however, over 80% of mining projects are often delayed2. Ensuring a stable lithium supply for the growing EV market remains a complex challenge.
The planet possesses sufficient lithium reserves for our foreseeable green-energy requirements. However, the practical process of extracting and utilizing this valuable resource remains a significant challenge.
Lithium and Electric Vehicles
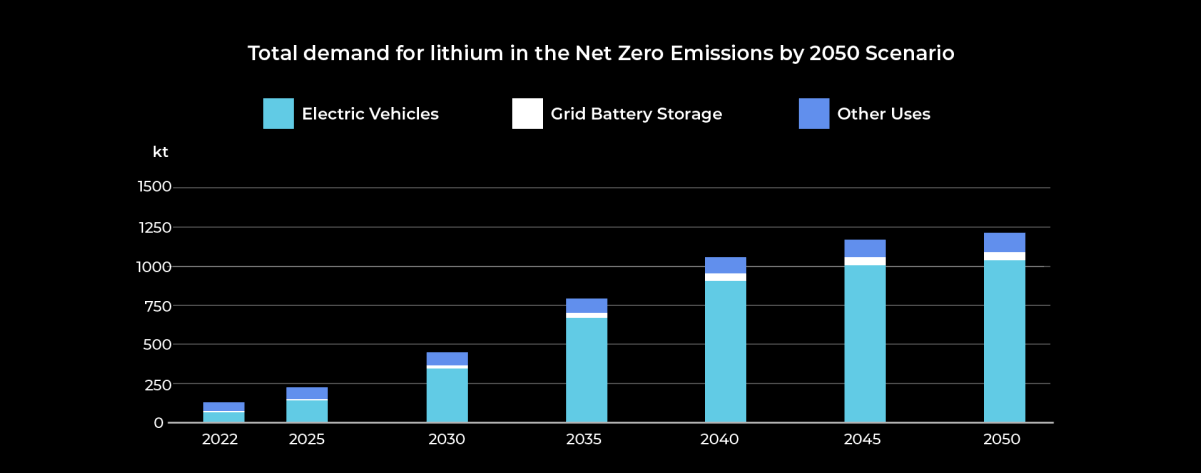
Source: International Energy Agency - Critical Minerals Market Report 2023
In 2022, electric vehicle (EV) sales surged by 60%, surpassing 10 million units, while energy storage systems experienced even more rapid growth with a doubling of capacity additions. Solar PV installations continued breaking records, and wind power was set for a resurgence after two slower years3. This incredible growth has led to a substantial rise in the demand for critical minerals.
China produces over 60% of global lithium, creating a globally reliant supply chain, even if batteries are made in the U.S. The U.S. has committed $2.8 billion in grants to expand electric vehicle battery production, part of it going to major auto suppliers, in an effort to secure domestic supply4. The American Battery Materials Initiative is another effort to ensure a stable supply of critical EV minerals. These initiatives aim to make EVs 50% of U.S. vehicle sales by 2030, spurring domestic manufacturing of EVs, chargers and batteries, aimed at making EVs affordable.
Uranium
Uranium, with atomic number 92 and symbol U, is a silvery-white metallic element with the highest atomic weight among naturally occurring elements. It's found in soil, rock, and water, and is extracted commercially from minerals like uraninite.
Uranium, with atomic number 92 and symbol U, is a silvery-white metallic element with the highest atomic weight among naturally occurring elements. It's found in soil, rock, and water, and is extracted commercially from minerals like uraninite. Discovered in 1789, it was initially used for colorants and later recognized for its radioactive properties. Its energy potential led to its use in nuclear reactors for electricity generation and in various industries globally.
The uranium market, pivotal for nuclear power, is undergoing significant shifts driven by supply-demand dynamics, geopolitics, and changing public attitudes. Governments are enacting pro-nuclear policies to meet net-zero climate targets, boosting demand. Factors such as emerging economies, advanced reactor tech, and small modular reactors are driving market growth. Amidst global efforts for clean energy and decarbonization, nuclear power is gaining recognition for its role, reshaping the uranium market.
During the recent World Climate Action Summit of the 28th Conference of the Parties to the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change, more than 20 countries from four continents announced their intent to triple their nuclear power capabilities.
THE ENERGY TRANSITION
Nuclear power can provide a stable source of energy during the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. In addition, its energy density (the amount of energy it contains per unit of mass) makes it significantly more powerful than other energy fuels1. For example, 1 kilogram of coal has an energy density of 44 megajoules, versus 1 kilogram of uranium (enriched to 3.5%) with an energy density of 3,900,000 megajoules - which would move an average vehicle 1,625 km, versus 18 m for the same vehicle running on crude oil.
Some of the key factors that are seeing nuclear taking a leading role in the energy transition are:
- Nuclear plants offer continuous, reliable baseload power, unlike weather-dependent renewables.
- Nuclear power is low-carbon, emitting no greenhouse gasses.
- Diversifying energy sources enhances security, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and imported energy.
- Ongoing R&D in nuclear technology, like SMRs, boosts safety, waste management, and efficiency, bolstering its role in the energy transition.
URANIUM PRICES
The increased demand for uranium stems from the growing popularity of nuclear energy, especially in countries like China and other emerging markets. Additionally, a significant portion of the uranium supply is situated in geopolitically sensitive regions, further driving up prices as speculative investors capitalize on this trend.
Uranium prices have skyrocketed to peak per-pound prices in January 2024, marking a milestone not seen in more than 15 years. This surge is attributed to a resurgence in nuclear power and disruptions in the supply chain, along with the introduction of physical uranium investment trusts into the spot market. SPROTT, a Canadian asset manager, launched its Physical Uranium Trust in August 2021, holding around 63.6 million pounds of U308.. Similarly, Zuri Invest AG launched its physical uranium investment trust in June 2023.
